Preliminary insights from AI-DAPT Demonstrators
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool, transforming various industrial sectors by enhancing efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. The AI-DAPT project showcases how AI can be integrated into diverse industrial applications to address specific challenges and create innovative solutions respectful of human rights. This post delves into the AI-DAPT approach and its implementation across four critical industrial demonstrators: Health, Robotics & Cognitive Ergonomics, Energy, and Manufacturing.
Health
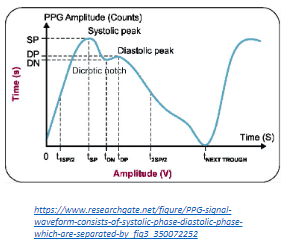
1. Health: Personalized Medicine through Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes mellitus is a global health challenge requiring continuous monitoring of blood glucose levels. Traditional methods are invasive and burdensome for patients. The AI-DAPT project addresses this issue by designing a non-invasive glucose monitoring system using AI-assisted analysis of photoplethysmography (PPG) curves. This approach leverages machine learning algorithms and pipelines to predict glucose levels accurately, making glucose monitoring more comfortable and less intrusive. The AI-DAPT solution will focus on creating wearable devices that provide real-time data on blood glucose levels, enabling better metabolic control and reducing the risk of complications. By integrating AI with PPG sensors, the system can potentially analyse data, identify patterns and offer personalised treatment plans, enhancing patient care and supporting early diagnosis and prevention of diabetes.
Robotics & Cognitive Ergonomics
2. Robotics & Cognitive Ergonomics: Human-Centred Automation. Manufacturing processes are becoming increasingly digitalised, but the role of human workers remains crucial. The AI-DAPT project emphasises human-centred automation, integrating human factors into digital representations and simulations. This approach aims to improve flexibility and responsiveness in manufacturing by fostering human-automation symbiosis. The solution involves collecting real-time data on human behaviour, comparing it with historical data and incorporating specific human features, such as skills and emotional states. This data will then be used to create adaptive automation systems that enhance human-machine collaboration, optimise working conditions and improve productivity. AI-DAPT’s focus on dynamic adaptation and context-awareness ensures that automation technologies are tailored to the needs of workers, rather than forcing workers to adapt to the technology.

Energy
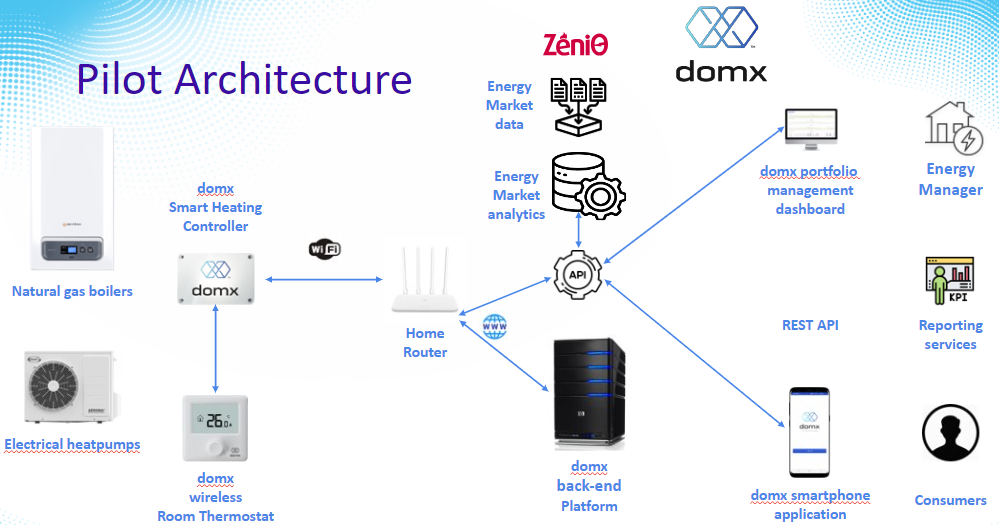
3. Energy: Cross-Vector Residential Demand Response through Smart Heating. The energy sector faces the challenge of improving efficiency and managing demand effectively. The AI-DAPT project addresses this by developing a smart heating system that utilises AI to optimise energy use in residential buildings. By analysing historical energy consumption data, weather conditions and user preferences, AI algorithms can predict energy demand and adjust heating systems accordingly. This approach not only enhances energy efficiency but also provides cost-effective solutions for energy suppliers and utilities. The AI-DAPT solution involves creating hybrid predictive models that adapt to new data, ensuring accurate demand forecasting and personalised energy management. This leads to better portfolio management, competitive energy prices and reduced energy consumption, contributing to sustainability goals.
Manufacturing
4. Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance of Production Assets. In the manufacturing sector, the availability of production equipment is critical for ensuring timely and cost-effective processes. The AI-DAPT project focuses on predictive maintenance, using AI to forecast and plan maintenance activities. By equipping tools with sensors and communication technology, valuable data on equipment performance can be collected and analysed. The AI-DAPT solution will include intelligent, automated maintenance systems that adapt to changes in tools, stakeholders and processes. This approach improves maintenance quality, reduces downtime and enhances the efficiency of maintenance processes. By leveraging AI for forecasting and planning, the project aims to create more accurate, resource-efficient and user-friendly maintenance models, ultimately enhancing productivity and reducing costs.

Conclusion
The AI-DAPT project exemplifies how AI can be harnessed to address specific industrial challenges and drive innovation across various sectors. By focusing on personalised medicine, human-centred automation, smart energy management and predictive maintenance, AI-DAPT will demonstrate the transformative potential of AI. These solutions not only enhance efficiency and productivity, but also contribute to sustainability and improve the overall quality of life. As European industries continue to evolve, the integration of AI will play a crucial role in shaping the future, enabling smarter, more responsive, and human-centric processes. The AI-DAPT project provides a blueprint for how AI can be effectively utilised to create meaningful and impactful solutions in the industrial landscape.